Introduction
Attrities is a commonly searched term online, often referring to arthritis, a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Arthritis is not a single disease but a broad term used to describe joint inflammation that causes pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced mobility. As people increasingly search for health information online, keywords like “attrities” attract significant organic traffic—making it an important topic for educational and health-focused websites.
In this article, you’ll learn what attrities (arthritis) is, its main causes, common symptoms, different types, diagnosis methods, treatment options, natural remedies, and lifestyle changes that can help manage the condition effectively.
What Is Attrities (Arthritis)?
Attrities, medically known as arthritis, is a condition characterized by inflammation of one or more joints. It can affect people of all ages, including children, although it is more common in older adults. The condition often leads to pain, stiffness, swelling, and limited movement in the affected joints.
Arthritis can impact any joint in the body, but it most commonly affects:
-
Knees
-
Hips
-
Hands
-
Spine
-
Shoulders
Over time, untreated attrities can reduce mobility and significantly impact quality of life.
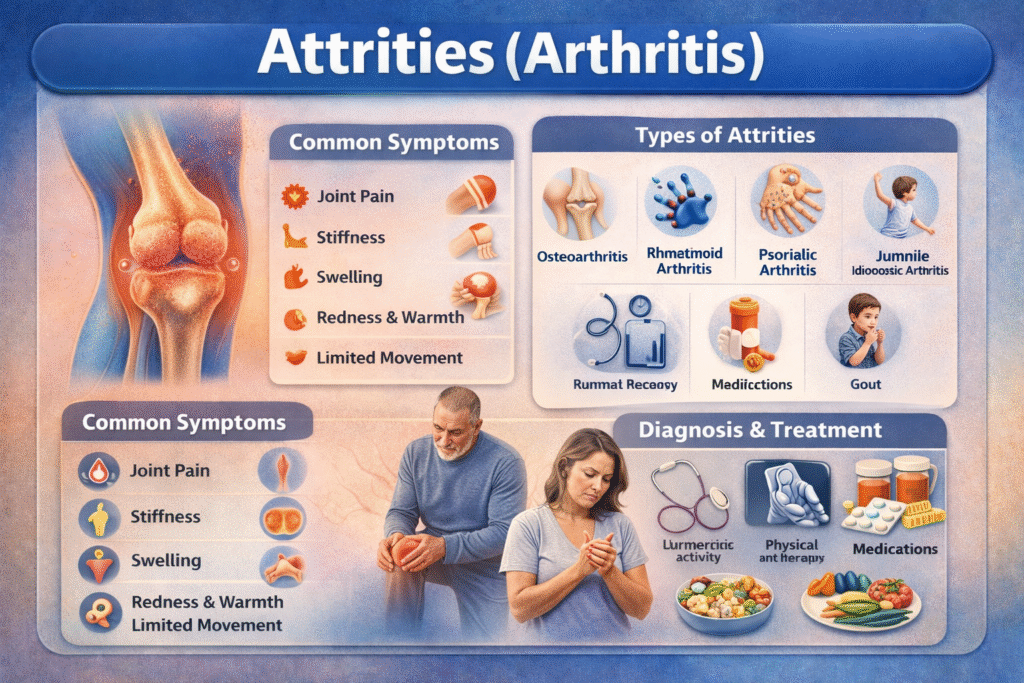
Common Symptoms of Attrities
Symptoms of attrities vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, but the most common signs include:
Joint painStiffness (especially in the morning)Swelling around jointsRedness and warmthReduced range of motionFatigue in inflammatory types of arthritisDifficulty performing daily activities
In early stages, symptoms may be mild and come and go. In more advanced stages, joint damage can become permanent.
Types of Attrities (Arthritis)
There are over 100 different types of arthritis, but the most common forms include:
1. Osteoarthritis
This is the most common type of attrities and occurs due to wear and tear of cartilage over time. It mainly affects older adults and often impacts the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the joints. It causes inflammation, pain, and joint deformity if left untreated.
3. Psoriatic Arthritis
This type is associated with psoriasis, a skin condition. It can affect joints and cause swelling in fingers and toes.
4. Gout
Gout is caused by uric acid crystal buildup in joints, often affecting the big toe. It can cause sudden and severe pain attacks.
5. Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
This affects children and teenagers, causing chronic joint inflammation and growth problems in severe cases.
Causes and Risk Factors of Attrities
The exact cause of attrities depends on the type, but common contributing factors include:
-
Aging and joint wear
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Autoimmune disorders
-
Obesity (increased stress on joints)
-
Joint injuries
-
Repetitive joint use
-
Infections (in some inflammatory types)
Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, smoking, and lack of physical activity can also increase the risk or worsen symptoms.
How Attrities Is Diagnosed
There is no single test to diagnose attrities. Doctors typically use a combination of:
-
Physical examination
-
Patient medical history
-
Blood tests (for inflammatory arthritis)
-
X-rays or MRI scans
-
Joint fluid analysis
Early diagnosis is crucial because timely treatment can slow disease progression and prevent permanent joint damage.
Best Treatment Options for Attrities
Although there is no permanent cure for most types of attrities, treatments focus on managing pain, reducing inflammation, and improving joint function.
1. Medications
Common medications include:
-
Pain relievers
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
-
Corticosteroids
-
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
-
Biologic agents for autoimmune arthritis
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy helps strengthen muscles around the joints, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. Regular guided exercises can significantly improve mobility.
3. Lifestyle Changes
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Low-impact exercises like swimming or walking
-
Using supportive devices (braces, orthotics)
-
Avoiding repetitive joint stress
4. Surgical Options
In severe cases, joint replacement or repair surgery may be recommended, particularly for hips and knees.
Natural Remedies and Home Management for Attrities
Many people with attrities look for natural ways to manage their symptoms. While these don’t replace medical treatment, they can help reduce discomfort:
-
Hot and cold therapy
-
Gentle yoga and stretching
-
Anti-inflammatory diets (rich in omega-3s, fruits, and vegetables)
-
Turmeric and ginger
-
Adequate sleep and stress management
Consistency is key when using lifestyle and natural approaches for long-term relief.
Attrities and Quality of Life
Living with attrities can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Chronic pain may lead to fatigue, anxiety, and depression. Support from healthcare providers, family, and online communities can make a big difference in coping with the condition.
Adopting adaptive tools, ergonomic furniture, and pacing daily activities can help individuals maintain independence and productivity.
How to Prevent or Reduce the Risk of Attrities
While some forms of attrities cannot be prevented, you can reduce your risk by:
-
Staying physically active
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Protecting joints from injury
-
Eating a balanced, anti-inflammatory diet
-
Avoiding smoking
-
Getting regular health checkups
Early lifestyle changes can delay the onset and progression of joint problems.
Final Thoughts
Attrities (arthritis) is a widespread condition that affects millions of people and can significantly impact daily life. With early diagnosis, proper treatment, and healthy lifestyle choices, many people successfully manage their symptoms and continue living active, fulfilling lives. Understanding the causes, types, and treatment options empowers individuals to take control of their joint health.
If you or someone you care about experiences persistent joint pain or stiffness, seeking medical advice early can prevent long-term complications.